Hotwell Boiler feedwater cascade tank
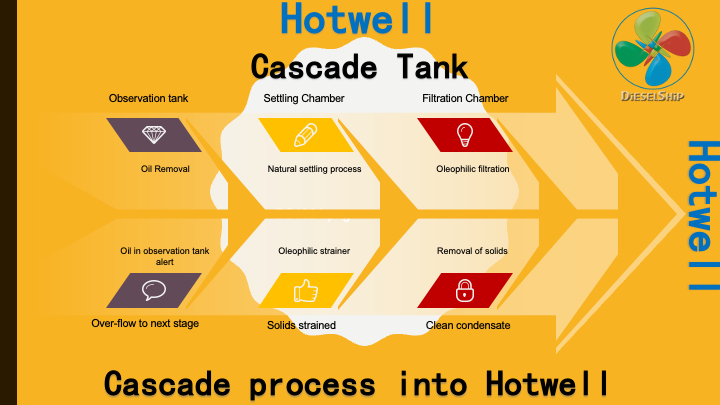
Hotwell Boiler feedwater cascade tank
Video Animation of Hotwell functioning
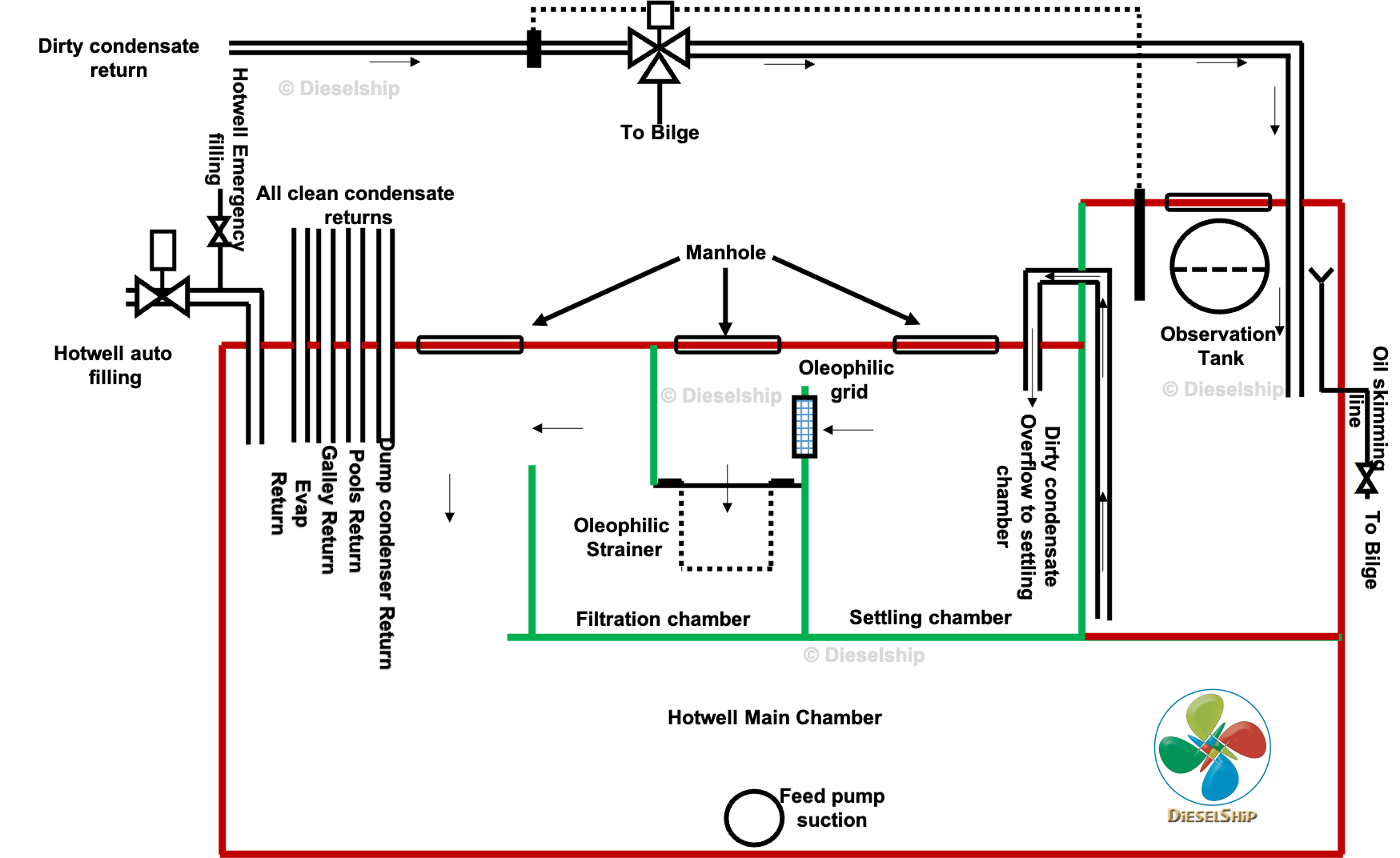
hotwell construction
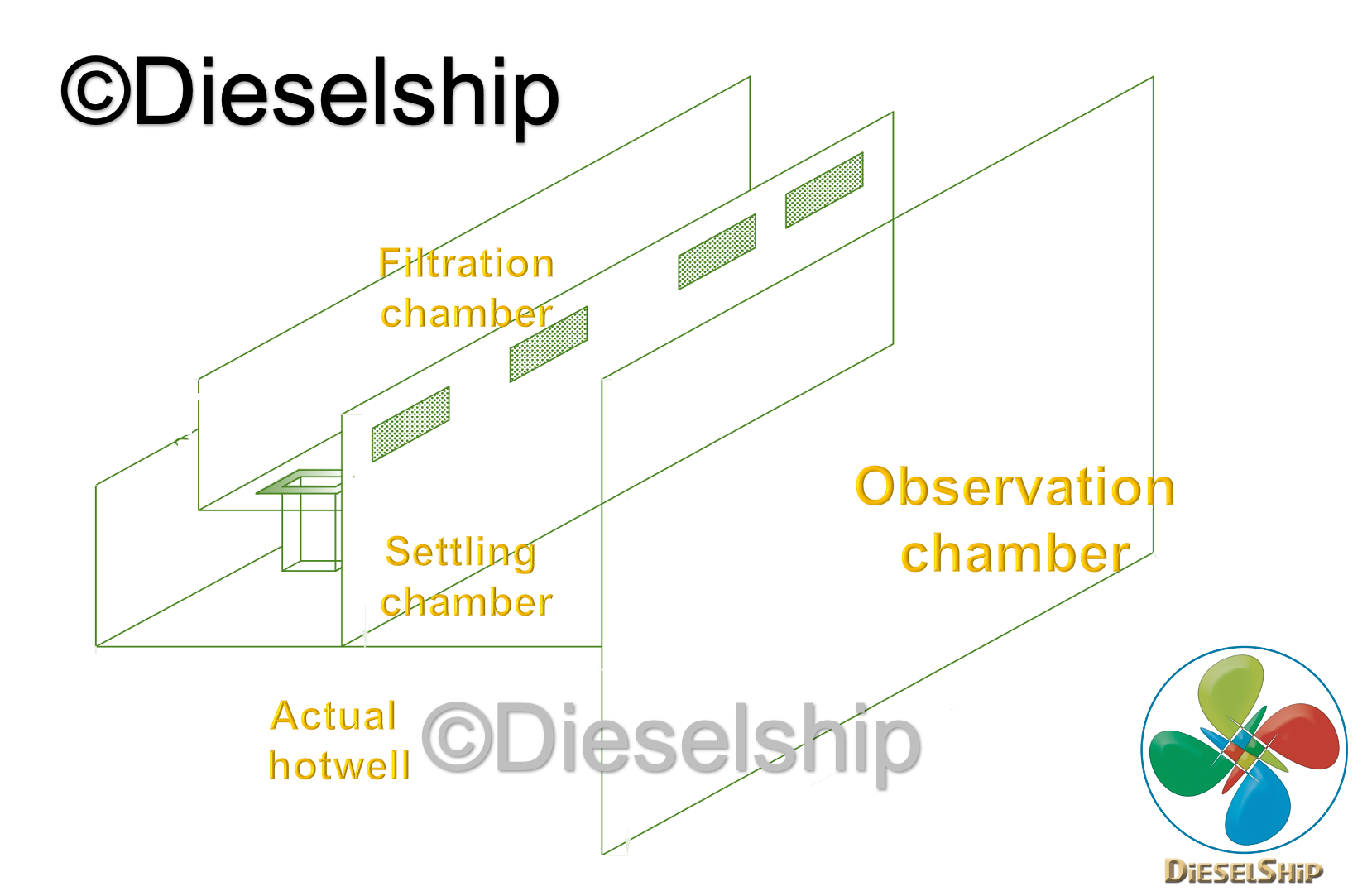
2D Image of internal construction
Introduction
Hello, You have reached this page most probably looking out for some information about hotell / cascade tank. I have been searching online for many months to repair a leaking hotwell in one of the ships i served. I wanted the internal drawing of the Hotwell, tried in many sources including the yard where the ship was built, but with No luck.
Finally i ended up opening my ship’s hotwell made measurements and learnt its operation. I am sharing my drawings and animation with you here.
I am not going to talk about hotwell functions here, just the construction and working of it.
Hotwell Boiler feedwater cascade tank construction
>> Hotwell is made of steel thickness about 10 mm plate. Obviously due to fire restrictions and class regulation it cant be stainless or other material.
>> Let me explain the parts and mountings of the cascade tank below.
Observation tank
>> Boiler observation tank receives the dirty condensate. Dirty condensate is nothing but the condensate returning from fuel , lube, purifier heaters, fuel tank, cargo tank heaters etc. This is called dirty condensate and isolated from the clean system. Dirty condensate is filtered in the hotwell using cascade method.
>> The tank itself is called an “hotwell”, Reason for naming it so is explained in detail later. The term cascade is often used because the dirty condensate is filtered through cascading method in different chambers.
>> Dirty condensate doesn’t readily have any contamination, however, due to failure of any heating coils oil may reach the system which then contaminates the whole system, to avoid such situation dirty condensate is treated in cascading process.
Oil sensing & Diverting 3-way control
>> The dirty condensate is installed with oil sensing probe in the main manifold (which manifolds all return into one header) and connects to the hotwell. This oil sensing probe (usually of capacitance type) monitors the return condensate, incase of any oil particles it will trigger an alarm and turn the diverter 3-way valve to the bilge, hence the contaminated water is diverted to bilge safeguarding the feed system from contamination.
>> The alarm alerts the watch keeping engineer who can check if the oily content is factual! trust me most of the times i have seen this sensor going Koo-Koo (Word typically used in cruise ships, to describe malfunctioning or kind of acting crazy or being confused) and creating false alarm.
>> If the alarm is not false, then the watch keeping engineer will go about shutting down the steam to all dirty heaters and investigating the root cause to identify the culprit and isolate.
Sight glass with light
>> The observation tank is installed with a sightglass and a light. This sight glass shows the top layer of condensate in the observation tank. The light installed shows clearly the appearance of this top layer. It is usual for the watch keepers to check for any traces of oil through the sight glass.
>> Yes, at some instances i have seen oil in observation tank but the sensor doesn’t pick this up! it is always a good watch keeping practice to monitor this sight glass as part of engine room rounds.
Skimming valve
>> The observation tank is also installed with a skimming line, which is pointing upwards with a funneled mouth. The mouth stays on the brink of the water level and the pipe leading outside the hotwell goes to a bilge well and installed with a valve.
>> Incase of any oil is seen in the sight glass this valve can be opened to skim the oil from the top layer of observation compartment.
Overflow line
>> The observation chamber overflows into the next chamber which is called as “Settling chamber”.
>> The overflow pipe is led from the bottom of the observation tank. Due to density difference the oil stays on top and water at the bottom hence, the overflow happens from the bottom of the observation compartment.
Settling Chamber
>> The next compartment on the hotwell tank or cascade tank is settling chamber, This compartment is provided to settle down any heavier particles such as solids and other impurities.
>> Here, the water is allowed to settle down. This chamber is isolated from the fluid movement from the rest of the compartments to ensure the settling process is not disturbed allowing it to naturally settle down.
>> The water from this compartment overflows from top via a oleophilic grid strainer.
Oleophilic
>> Oleophilic means – having a strong affinity for oils rather than water.
>> The strainer made of such material is installed here which absorbs the oil and also prevents solid particles from moving in to the next chamber.
>> There is a manhole on top of this chamber, to inspect and clean or replace the strainer.
Filtration chamber
>> The next compartment is Filtration chamber, the water overflows from settling chamber. This filtration chamber is installed with fine mesh filter which is of oleophilic nature. These filters ensure both oil & solid particles are completely removed from the water that passes to the next compartment.
Hotwell OR Main chamber
>> The next compartment is the actual “hotwell” where the condensate water gets stored and the boiler water feed pump takes suction from.
>> The word “Well” originates from this compartment because olden days!! the hotwell used to be of 2 compartments one of which used to be a open tank on top, where all condensate return, then gets filtered using natural filtration materials such as stones, coarse sand, pebbles etc.
>> The filtered water from the open tank on top drains through filtering materials down into a ‘Well’ like tank below from where the water was taken to fill the boiler.
Clean condensate return
>> The clean condensate usually from swimming pool heaters, potable / domestic water heaters, return from evaporator, return from galley etc are connected to this chamber.
>> Since clean condensate may not have any oil contamination, it is allowed to be drained straight into the hotwell.
Hotwell temperature
>> It is a very usual question asked by examiners as to why hotwell temperature is critical? Why hotwell temperature is maintained higher? and at what temperature the hotwell is maintained?
>> The answer is “Dissolved Oxygen”. Yes, the oxygen is key to any living being! however, we discourage oxygen in boiler water! because dissolved oxygen in boiler water aggravates corrosion of boiler tubes, shell and the drum!
>> To remove dissolved oxygen from the water the hotwell temperature has to be maintained above 85oC. At this temperature the Dissolved oxygen saturation is very low, hence use of oxygen scavenger chemical consumption is highly reduced.
How to increase hotwell temperature?
>> By the hot condensate (by passing the condenser).
>> The clean condensate is usually condensed as water using an atmospheric condenser or drain cooler which is cooled by fresh water. Mostly in cargo ships, i have see atmospheric condenser however in large passenger vessels drains cooler is used, the cooling medium used here is the LT fresh cooling water system.
Hotwell filling
>> Hotwell Boiler feedwater cascade tank level is automatically maintained using a automatic filling valve which is controlled by float switches. the float switches read the water level and control opening / closing of the valve. A PID controller is used where the steam demand is very high such as Oil tanker and cruise ships.
Emergency filling
>> There is also a provision for manual filling of hotwell. This is provided to fill the hotwell if the hotwell level is dangerously low and the supply through automatic filling is inadequate or auto filling system malfunctioning.
Very important:
As i mentioned earlier these are my year long learning by entering the hotwell myself and by talking to shipyard engineers. If you have additional information or correction please do so, i am always happy to correct myself and learn new things! Hope this helps.

very helpfull article in time of home self study in this pandemic
Nice explanation
It was very helpful. Thank you so much.
Thank you. Glad it was helpful to you.
If oil is seen in the observation tank how to find from where it is leaking
I wish it is as easy as you ask! well, if you find oil in observation tank you have to start tracing the leak systematically. You can start by isolating individual circuits one by and see if the oil return stops!
Otherwise, just hit the most usual culprit, The ‘Frequent flyers’ 🙂 like the purifier heaters, fuel heaters etc! Isolate the steam supply and open the top bonet (if provided) of the steam trap to see if you see oily residue.
It is a bit time consuming and can be irritating at times but you can definitely find the leaky ones if you start to isolate all and then open one by one or close one by one and see if the leak stops!
Hope this helps.
It is generally coming from some fuel oil or lub oil heater. First check what oil is it…then say it’s fuel oil, check the drain of the steam traps of the oil heaters one by one. Whichever shows traces of oil is the culprit.
fist of all find out type of oil weather lub oil or fuel oil,once the type of oil is confirmed then check the equipment recently put in use. if not then check at outlet of heater or tank in return line.in return line at outlet we always have drain valve open that one and check for oil leakage.
I want know that, all pure condensate has separate lines as shown in your diagram. Why the dump condenser is there, by where it will get a steam return sir?
Dump condenser is to dump excess steam produced. This usually happens when the exhaust gas boiler is in operation. To keep the steam pressure within safe limit excess steam is dumped in dump condenser which is usually sea water cooled.
Hope this helps.
Yes sir, I got the point. Thanks for your kind reply!!
Nice explanation
If cascade tank produces too much vapor/steam on its overflow vents located in filtration chamber and it is strongly goes out in the manhole of filtration chamber(because we open it always for inspection) what can we do to rectify it? What can we check specially when we are in cold areas where fresh air flows to vents which produces alot of condensate on floor, is it directly steam traps to be ?
Why are steam lines present in the cascade tank? Is that how the temperature is maintained in the tanks?
Cascade tank temperature is maintained by dumping the hot condensate into the cascade tank without cooling; The dump condenser has a bypass valve which is controlled to maintain the cascade tank temperature above 90 deg celsius.
This temperature is required to evacuate dissolved oxygen in water, Dissolved oxygen causes pitting and other corrosion in boiler drum and pipelines.
Now, imagine a situation where the condesate return is not hot enough, or there is no steam usage hene no consensate return! The cascade tank will have no heating! in such cases the cascade tank is heated by steam coils to maintain 90 deg or above temperature. Hope this explains.
I want to ask ,please, why more steam than water in hot well ?,
Thank very much . It is very help full .
Thank you very much .it is very helpful .
the HW low water level alarm SHOULD BE SPECIFIED IN ABOVE ARTICLE
Nice explanation, please come up with more explanations in future..
How do I reduce the temperature of the hotwell as it it is going above 90 degress
Hello,
Your hot well temperature can increase due to two main reasons:
Steam Heater Leakage: The steam heater installed in the hot well may be passing, causing steam to leak into the water and heat it up.
Bypass Issues in the Condensate Return Line:
The condensate cooler or atmospheric condenser, which is part of the condensate return line, may be bypassed. Normally, the bypass valve is slightly open to allow some hot condensate to return directly to the hot well to maintain its temperature. However, if this valve is opened too much or is passing, excessive hot condensate will enter the hot well.
If you believe the bypass is closed but the cascade tank is still overheating, the heat exchanger (condensate cooler/atmospheric condenser) might not be functioning effectively. This could be due to fouling, a clogged passage, or insufficient cooling water supply.
Additionally, sometimes the bypass valve is only slightly open, but due to valve malfunctions or blockages, the return condensate bypasses the heat exchanger entirely.
Check each of these possibilities step by step to identify the root cause.
All the best!