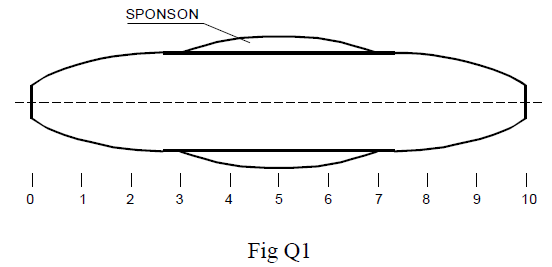
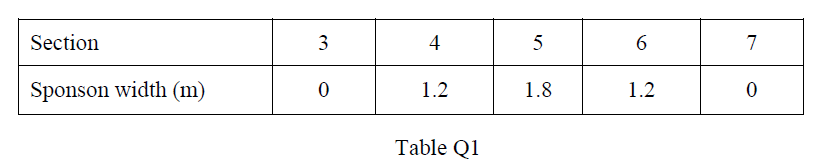
Question Topic: Numerical Question
Q8. The 1/2 ordinates of a waterplane 120 m long are as follows: (16)
Calculate: (a) Waterplane area(b) Distance of centroid from midships.
Section AP 1/2 1 1½ 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 8½ 9 9½ FP ½ ord 1.2 3.5 5.3 6.8 8 8.3 8.5 8.5 8.5 8.4 8.2 7.9 6.2 3.5 0m
Page 31 of 40